National Center for External Evaluation of Education
Overview of Education System
In the Republic of Croatia, the Ministry of Science, Education, and Sports (MSES)1 is responsible for the administration of the education system and provides the greatest financial support, among funding bodies, to the education sector. In addition to the MSES, other ministries and local governments allocate funds to education. The education system in the Republic of Croatia comprises educational cycles (presented in Exhibit 1) as follows:
- Preschool education encompasses education and childcare for children ages 6 months to 6 years, and is delivered through educational, health, nutritional, and social care programs2
- Primary education (Grades 1 to 8) is compulsory and free for all children ages 6 to 153
- Secondary education (Grades 1 to 4) includes the following types of secondary school: gimnazija (general or specialized), vocational or trade schools, and art schools (music, dance, visual arts, etc.)
- Higher education comprises university or professional studies, which are undertaken at universities or polytechnics and schools of professional higher education, respectively
Exhibit 1: Educational Cycles for Acquiring Key Competences
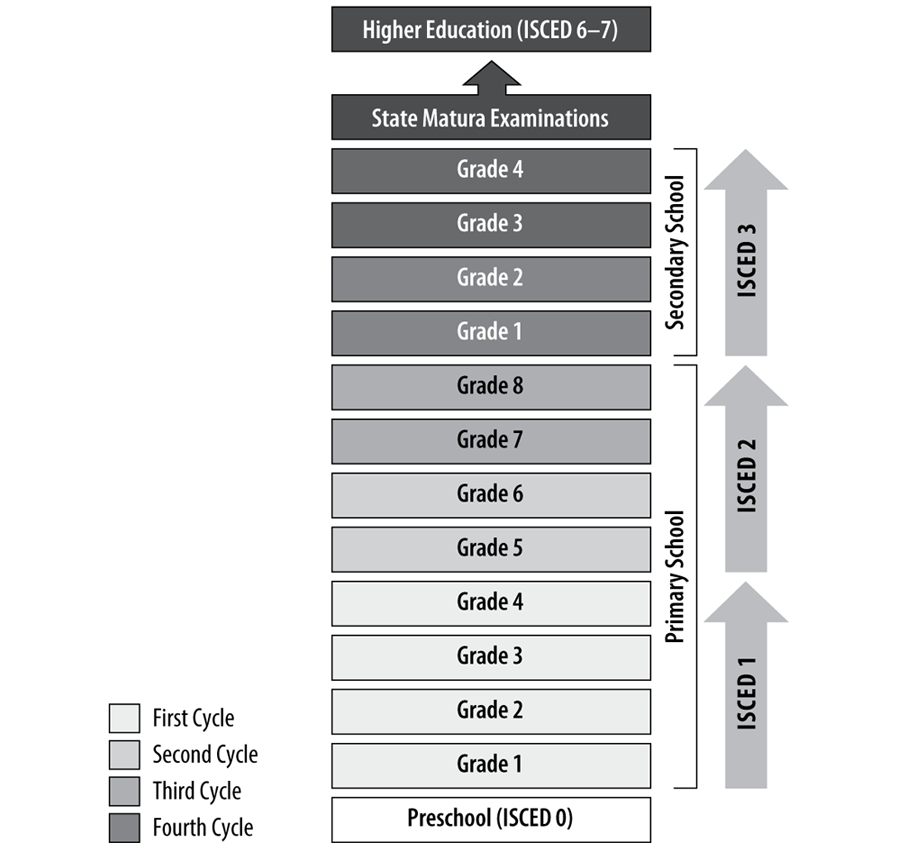
Educational cycles are periods of educational development, which together comprise a student’s entire general education. They are based on the developmental phases of students and share common educational goals. The National Curriculum Framework in Croatia establishes four educational cycles in which students acquire key competences:4
- The first cycle comprises Grades 1 to 4 of primary school
- The second cycle comprises Grades 5 to 6 of primary school
- The third cycle comprises Grades 7 to 8 of primary school
- The fourth cycle comprises Grades 1 to 2 of secondary vocational and art school, or Grades 1 to 4 of secondary grammar school (gimnazija)
It should be noted that at secondary vocational and art schools, general educational content may be taught in Grades 3 to 4, as well, depending on the profile of the school and the needs of the students. If the fourth cycle is completed at a secondary vocational school, it results in the lowest level vocational qualification, which means that students may acquire their first vocational qualification at age 16.
Languages of Instruction
The official language in the Republic of Croatia is Croatian. In certain areas of Croatia, where ethnic minorities comprise a majority of the population, the minority language is recognized as a second official language. In Croatia, the languages of instruction may be categorized into two groups: so-called territorial or minority languages, and nonterritorial languages (in accordance with the European charter on regional or minority languages).5
Members of national minorities are guaranteed the right to education in their native language and can exercise their constitutional right to education in their native language via three basic models:
- Model A Schools—Classes are conducted in the minority language, and study of the Croatian language is compulsory for the same number of hours in which instruction is conducted in the minority language (Czech, Hungarian, Serbian, and Italian)
- Model B Schools—Classes are conducted in two languages, with science subjects taught in Croatian and social science subjects taught in the minority language (Czech or Hungarian)
- Model C Schools—Classes are conducted in Croatian, and an additional two to five school hours are dedicated to fostering the language and culture of national minorities (Albanian, Austrian, Czech, Hungarian, Macedonian, Slovak, Slovene, Serbian, Ukrainian, and Rusyn